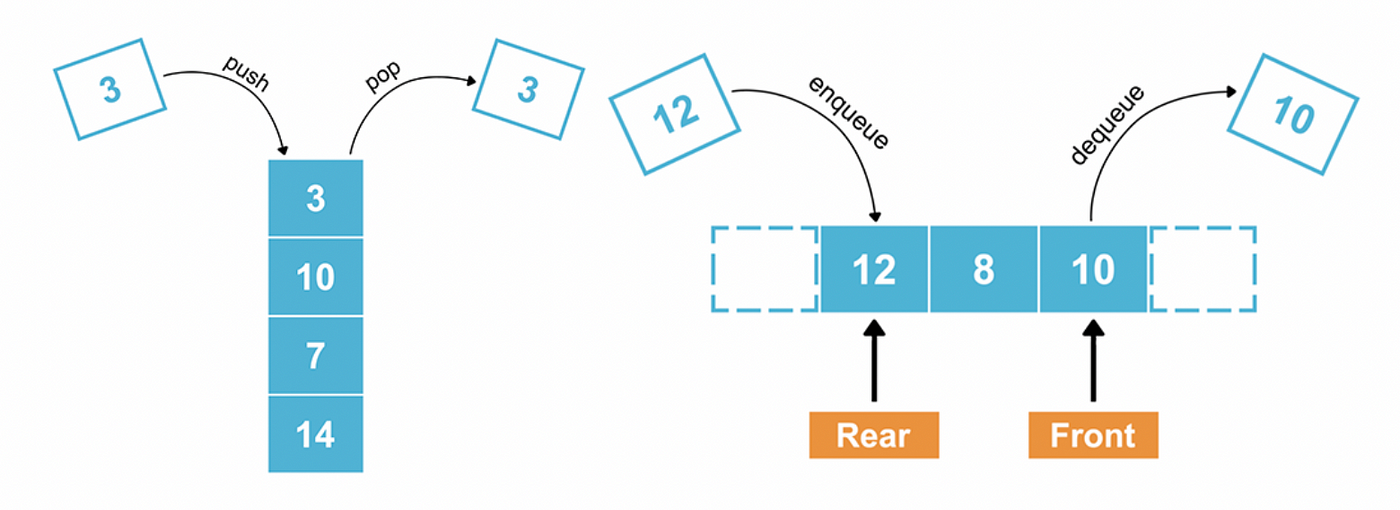
Stack and Queue
In Python, a stack and a queue are two common data structures used for managing collections of items, but they operate differently in terms of how items are added and removed:
- Stack:
- A stack is a data structure that follows the Last-In-First-Out (LIFO) principle.
- It resembles a stack of plates, where the last plate added is the first one to be removed.
- In Python, you can implement a stack using a list. You typically use the
append()method to push items onto the stack and thepop()method to remove and retrieve the top item.
Example:
stack = [] stack.append(1) # Push 1 onto the stack stack.append(2) # Push 2 onto the stack top_item = stack.pop() # Pop the top item (2) - Queue:
- A queue is a data structure that follows the First-In-First-Out (FIFO) principle.
- It resembles a line of people waiting in a queue, where the first person to join the line is the first one to be served.
- In Python, you can implement a queue using the
dequeclass from thecollectionsmodule, which provides efficient operations for adding and removing elements from both ends of the queue.
Example:
from collections import deque queue = deque() queue.append(1) # Enqueue 1 queue.append(2) # Enqueue 2 front_item = queue.popleft() # Dequeue the front item (1)
In summary, a stack follows the LIFO principle, while a queue follows the FIFO principle. Depending on your specific use case and requirements, you can choose to use either a stack or a queue in Python to manage and manipulate your data.
As above, in Python, ‘list’ is basically a ‘stack’ method, and when using a ‘queue’ method, it can be used by ‘import’.
However, since we have to consider all languages, let’s also look at how to implement it directly through ‘class’.
To implement a stack in a computer language, you can use various data structures and techniques, but I’ll provide a simple example in Python using a list. A stack can be easily implemented using a list with the following basic operations:
- Push: Add an element to the top of the stack.
- Pop: Remove and return the element from the top of the stack.
- Peek (or Top): View the element at the top of the stack without removing it.
- isEmpty: Check if the stack is empty.
Here’s a Python implementation of a stack using a list:
class Stack:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def push(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def pop(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items.pop()
else:
raise IndexError("Pop from an empty stack")
def peek(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items[-1]
else:
raise IndexError("Peek into an empty stack")
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
Here’s how you can use this Stack class:
stack = Stack()
stack.push(1)
stack.push(2)
stack.push(3)
print("Stack:", stack.items) # Output: Stack: [1, 2, 3]
top_item = stack.pop()
print("Popped item:", top_item) # Output: Popped item: 3
print("Stack after pop:", stack.items) # Output: Stack after pop: [1, 2]
print("Is the stack empty?", stack.is_empty()) # Output: Is the stack empty? False
print("Top item of the stack:", stack.peek()) # Output: Top item of the stack: 2
print("Size of the stack:", stack.size()) # Output: Size of the stack: 2
This Python Stack class provides a basic implementation of a stack using a list, but you can adapt the concept to other programming languages by using appropriate data structures and methods based on the language’s features and conventions.
Below is the implementation of ‘queue’.
class Queue:
def __init__(self):
self.items = []
def enqueue(self, item):
self.items.append(item)
def dequeue(self):
if not self.is_empty():
return self.items.pop(0)
else:
raise IndexError("Dequeue from an empty queue")
def is_empty(self):
return len(self.items) == 0
def size(self):
return len(self.items)
This Queue class provides a basic implementation of a queue using a list with the following operations:
- Enqueue: Add an element to the rear of the queue.
- Dequeue: Remove and return the element from the front of the queue.
- isEmpty: Check if the queue is empty.
- Size: Get the number of elements in the queue.
Here’s how you can use this Queue class:
queue = Queue()
queue.enqueue(1)
queue.enqueue(2)
queue.enqueue(3)
print("Queue:", queue.items) # Output: Queue: [1, 2, 3]
front_item = queue.dequeue()
print("Dequeued item:", front_item) # Output: Dequeued item: 1
print("Queue after dequeue:", queue.items) # Output: Queue after dequeue: [2, 3]
print("Is the queue empty?", queue.is_empty()) # Output: Is the queue empty? False
print("Size of the queue:", queue.size()) # Output: Size of the queue: 2
This Python Queue class provides a basic implementation of a queue using a list, but you can adapt the concept to other programming languages by using appropriate data structures and methods based on the language’s features and conventions. In practice, for more efficient implementations, you might want to use a deque from the collections module or utilize specialized queue data structures available in your programming language’s standard library.